At present, high-alumina bricks and low-cement castables are mostly used for masonry in the furnace roof of aluminum industry kilns. In order to speed up the smelting speed and save energy, light bricks, light refractory castables, and refractory fiber products are generally used as thermal insulation layers. High-alumina bricks for the roof of aluminum industry kilns are sold in Venezuela. It can be seen from the use of lining materials for kilns in the foreign aluminum industry, that low-cement castables have become the mainstream products of refractory materials for kilns and furnaces in the aluminum industry due to their good spalling resistance, good thermal shock resistance, and small surface pore size.

The aluminum melting furnace is one of the key-equipments in the aluminum processing and casting industry. The smelting process of aluminum is also the production link with the largest consumption of materials and energy in the aluminum processing industry. In order to increase output, aluminum melting furnaces are constantly being enlarged, and new smelting processes are emerging one after another. Thus, the quality of the refractory material directly affects the properties of the melt and the cost of smelting. These changes also put forward new requirements for refractory materials for aluminum melting furnaces. Generally, unshaped refractory materials are used for the construction of furnace top refractories, and high-alumina anchor bricks are used for fixing.
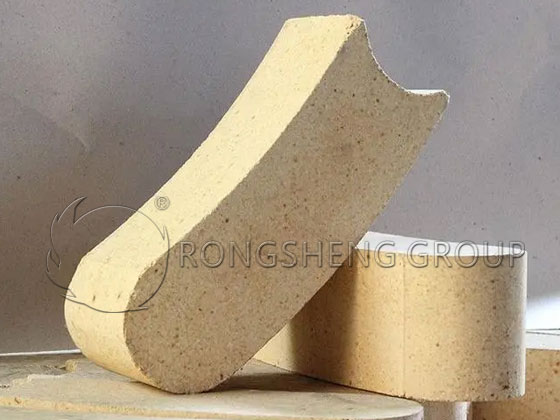
High Alumina Brick Anchoring Brick for Furnace Roof
Anchor bricks are also called hanging bricks. Anchor bricks are traction bricks or tension bricks for industrial furnaces. Especially when it comes to the anchoring bricks for industrial furnace roofs in the forging industry, the shape is cuboid, and the main body is divided into three parts: the upper part of the head, the middle neck, and the lower part of the rib. The middle neck is where the hanger is installed. Make the hook into the shape of a “door” and then align it, clamp the middle of the anchor brick and hang it on the I-beam. There is also a way to anchor the bricks with holes. There is a hole with a diameter of about 20mm at the head of this type of brick. Then make the screw into an L shape, pass one end through the hole and then tighten the nut, and hang the other end on the I-beam to tighten the nut. Judging from the shape of the current industrial anchor bricks, there are various types. But the ultimate purpose is the same, that is, it will be used as the tensile support of the top refractory castable to ensure the firmness and high-strength stability of large-scale pouring.

The hanging spacing of anchor bricks in the furnace roof is 400~500mm, 500mm horizontally and 400mm vertically. During construction, the inner surface of the castable and the top surface of the anchor brick should be kept on the same vertical plane as possible. The hanging size can also be adjusted appropriately according to the gravity point. When hanging on the stovetop, it is mostly cast as a whole or rammed with refractory plastic. The form of the furnace roof is divided into a flat roof and a vault. The vault is generally made of refractory castables, and the flat roof can be made of refractory plastic. No matter which construction method is adopted, the anchor bricks should be set with different expansion joints, and should not be directly dry poured without any expansion joints reserved. The raw materials used in the production of anchor bricks are generally products made of aluminum-silicon materials, and the residual crystalline SiO2 quartz will expand to a certain amount at a certain temperature. The common way to reserve expansion joints is to apply black asphalt paint on the outer surface of the anchoring brick.

The shape and connection method of anchor bricks are different, and the size is also different. The most commonly used anchor bricks are 330mm, 380mm, 440mm, and 500mm in height. But anchor bricks are available with and without holes, and those with holes are generally used in furnace walls. The ones without holes are used on the stovetop, which is the so-called hanging method, so they can also be called hanging bricks.
The material of anchoring bricks generally uses more grade 3 high alumina bricks, because the grade 3 high alumina bricks have good flexibility. There are also secondary high-alumina bricks and first-class high-alumina bricks. However, this is determined according to the difference in the use temperature of the furnace lining and the material of the refractory castable.

High-Quality Refractories for Aluminum Melting Furnace Lining
Before the 1960s, refractory bricks and refractory mortar were mainly used as furnace lining materials for aluminum melting furnaces. With the rapid development of the aluminum industry, the original furnace lining materials were gradually replaced by clay bricks. However, clay bricks are mainly composed of aluminosilicates, which are easily destroyed by reaction with molten aluminum, and high-alumina bricks combined with phosphate appear later. Later, due to the poor wear resistance of phosphate-high alumina bricks, the pore size is about 22um, and the surface pores are relatively large. At about 1100 °C, the combined decomposition of phosphate produces larger pores, and molten aluminum can easily penetrate into it, especially in the slag line, the erosion is more serious. And because the high alumina brick is mainly corundum phase, the thermal shock resistance is poor, and the siliceous component in the composition is easy to be eroded. In practice, the average lifespan of furnace villages built with high-alumina bricks is only about 3 years, and they tend to be gradually replaced by castables. Buy high-quality refractory materials for aluminum melting furnaces, such as non-stick aluminum castables, anti-seepage materials for aluminum melting furnace bottoms, etc. Contact us for free samples and quotes.